Simple Overview of the Neck
Differentials
When it comes to spine pain, exposing pain generators (a la CRISP, if you will) can be very helpful to match treatment:
Neurogenic: Myelopathy, Radiculopathy, some headaches
Disc: Typical IVD presentation. Extent of damage variable
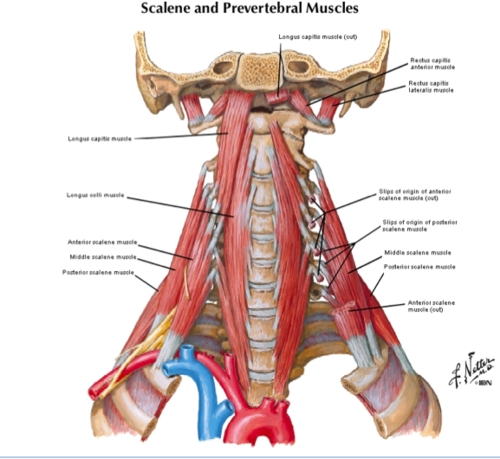
Muscles/Joint: Posterior and lateral pretty straightforward… remember the deep anterior neck flexors!
Systemic/Other: Rheumatic (AS, RA, DISH), Vascular, esophagitis, angina. Rule’em out!
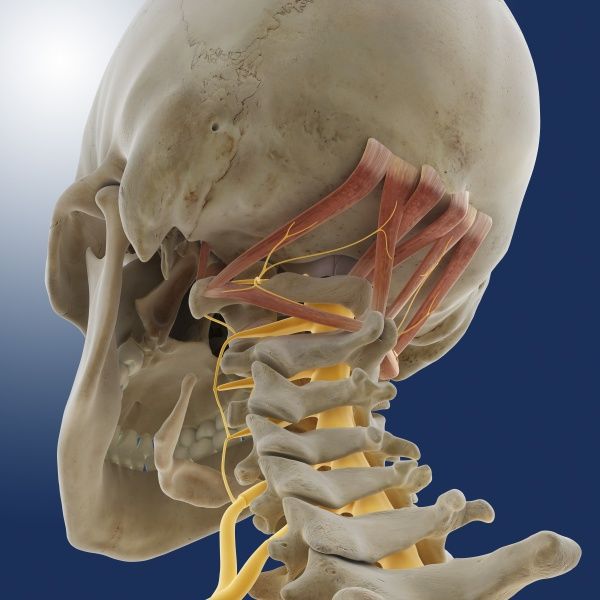
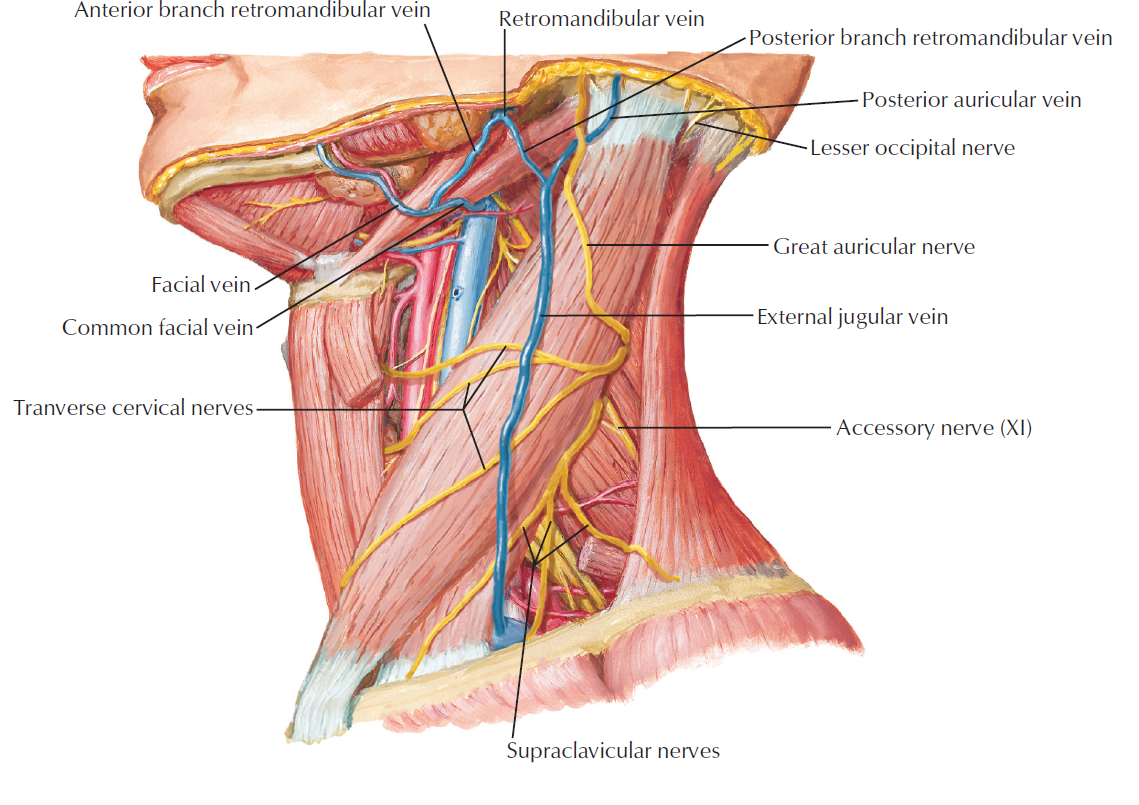
Anatomy
Thoughts
Most common cause of neck symptoms are biomechanics: Axial, WAD, Cervical Radiculopathy.
Axial neck pain has a high rate of spontaneous resolution. Presents similar to WAD except - WAD has associated trauma, often presenting with discopathy and possible radiculopathy.
Quebec Classification of WAD - 4 Categories
Grade 1 : general symptoms without objective findings
Grade 2 : general symptoms with musculoskeletal findings
Grade 3 : neck complaints with neurologic signs
Grade 4 : neck pain with fracture/dislocation
*Imaging recommended for WAD Grades 3 & 4, blunt trauma, axial pain unresponsive to 6-8 weeks of care. MRI recommended for suspected myelopathy, infection, CA, radicular pain with motor reflex deficit, radicular pain not resolved in 6 - 8 weeks (recommendation Grade B)
Radiculopathy presents with sharp & dermatomal distribution of symptoms (*Recall radicular pain vs. radiculopathy).
*TOS offered in separate blog
Assessments
Progressive cervical compression testing (Spurling’s) or each of each component parts assesses radicular symptoms. Pair with nerve tension testing - central & peripheral - for agreement.
End-range loading progressions for disc involvement.
Extension-Rotation testing for provocative joint mechanics.
O’Donaghue’s for evaluation of passive and active component of the region
Management
Review of Conservative Management for WAD grade II (low rating)
more effective for pain @ 6 mo, and 1-3 years
improved Cap mobility (horizontal plane) @ less than 3 months
active better than passive care @ 6 mo, and 1-3 years
no difference between early and late interventions